Blockchain is an innovative technology that provides a solution to this query. Envision a collective digital register that documents transactions across a cluster of computers rather than a solitary server. This register, known as a blockchain, is highly secure and resistant to tampering, ensuring that once data is inputted, it remains unalterable. Consequently, blockchain is exceptionally well-suited for monitoring valuable entities, ranging from financial dealings such as cryptocurrency to the ownership of assets like real estate or intellectual property.
Demystifying Blockchain: A Distributed Ledger
Blockchain fundamentally operates as a decentralized ledger system. Picture a vast spreadsheet that is replicated and dispersed among a cluster of computers. Each computer within the network possesses a duplicate of the spreadsheet, ensuring that any modifications made to it are promptly mirrored across all other duplicates.
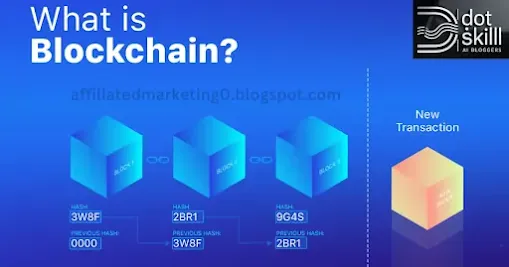
In essence, a blockchain is an ever-expanding series of records, known as blocks, which are interconnected securely through cryptographic methods. Every block includes a timestamp, transaction details, and a reference (cryptographic hash) to the preceding block.
You May Also Visit this: Data Entry
Screenshot:
Key Features of Blockchain
Here are some of the key features that make blockchain technology so unique and powerful:
Decentralization: The blockchain is not controlled by a single authority. It's a peer-to-peer network, meaning all participants have equal footing. This eliminates the need for a central authority, making it more secure and resistant to fraud.
Immutability: Once data is added to a blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted. This is because each block is cryptographically linked to the previous block. Any attempt to tamper with a block would corrupt the entire chain, making it easily detectable.
Transparency: All transactions on a blockchain are transparent and publicly viewable. Anyone can see the history of transactions on a blockchain network, which fosters trust and accountability.
Security: Blockchain uses cryptography to secure transactions. Cryptographic hashes and digital signatures make it very difficult to tamper with data on a blockchain.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Now that we understand the key features of blockchain let's take a look at how it works:
Initiating a Transaction. Upon initiation, a transaction on a blockchain network is disseminated to all participants within the network.
Verification: The transaction's validation is subsequently confirmed by the network participants. The method of verification may differ depending on the particular blockchain network. Occasionally, miners (designated nodes within the network) compete to decipher intricate mathematical problems to authenticate transactions. This procedure is commonly referred to as proof-of-work.
Adding a Block: Upon verification of a transaction, it is appended to a fresh block. This block includes a cryptographic hash of the preceding block, establishing a connection to the entire chain.
Adding the Block to the Ledger: The latest block is subsequently appended to the decentralized ledger, prompting all members of the network to synchronize their respective ledger copies.
This process persists as fresh transactions are initiated and validated. The blockchain ledger expands continuously, with each block firmly connected to its preceding ones.
Potential Applications of Blockchain
The potential of blockchain technology to transform numerous industries is significant.
Finance: Blockchain technology enables the creation of secure and transparent financial transactions, with applications ranging from optimizing cross-border payments to developing innovative financial products.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain technology enables the monitoring of goods as they move along the supply chain, leading to enhancements in transparency, efficiency, and traceability.
Voting Systems: Blockchain technology has the potential to establish secure and unalterable voting systems, ultimately decreasing voter fraud and boosting confidence in election processes.
Healthcare: Blockchain technology has the potential to enhance the storage and management of medical records, ensuring their security and facilitating efficient healthcare administration. By leveraging blockchain, patient care can be improved, and the overall healthcare system can be streamlined.
Identity Management: Blockchain technology has the potential to establish trustworthy and confirmable digital identities, thereby aiding in the mitigation of identity theft and fraudulent activities.
These are merely a handful of instances showcasing the potential applications of blockchain technology. As the technology progresses, we can anticipate the emergence of an even more significant number of inventive use cases.
The Future of Blockchain
Blockchain remains a nascent technology with the capability to revolutionize numerous industries. Its distinct characteristics enable the creation of secure, transparent, and efficient systems. With ongoing advancements in blockchain technology, its integration into various applications is inevitable.
Meta Description:
This guide aims to simplify the concept of blockchain technology. It provides an easy-to-understand explanation of what blockchain is, its characteristics, and the various ways it can be utilized in finance, supply chain management, voting systems, and other fields.



0 Comments